티스토리 뷰
고객이 생각하는 용량과 실제 사용할수 있는 용량이 차이가 난다. 왜일까?
- 엑사데이타 용량 계산법
Quarter Rack 의 경우
- 2 DB nodes
- 3 Storage Cells
3 Cell 서버 (High Performance) 는 아래와 같이 계산될수 있다.
Step 1: RAW 사이즈 계산
우선 전체 용량을 구해보면 아래와 같다.
전체 Raw 용량 => 각 Cell 당 12EA disk * 각 Disk 당 600G * 3 Cell
=> 21,600GB 또는 21.09TB
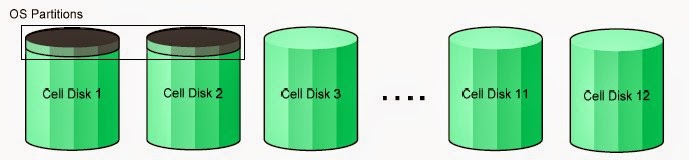
그런데 각 Cell 서버의 1번,2번 디스크에서 OS Linux 영역으로 30G씩 할당이 된다. 그래서 기본으로 디스크 그룹은 남은 10개의 디스크의 30G 용량으로 생성된다.
그리하여 DBFS 디스크그룹은 아래와 같이 용량을 차지 한다.
각 Cell에서 10EA 디스크 * 각 디스크에서 30 GB 씩 * 3 cell = DBFS => 900 GB
개별 디스크 600G-30G = 570G 가 사용가능하며 전체 디스크가 12EA * 3 cell 이므로
570 * 12 * 3 = 20,520 GB or 20.03TB
Step 2: 미러링을 고려해 보자
NORMAL Redundancy 로 설정하여 이중화 되었으므로 용량의 반만 사용할수 있다.
20.03/2 = 10.01TB.
Step 3: fault tolerance를 고려한 여유공간 확보
Disk Failure Coverage(DFC) 를 고려하면 Cell 에서 디스크하나가 나갔을 때를 대비한 용량은 600G 디스크 하나의 용량과 같다.
NOTE: that is a very important part. You need to plan for a Disk failure coverage or for complete cell node failure coverge. The ORACLE support document "Understanding ASM Capacity and Reservation of Free Space in Exadata (Doc ID 1551288.1)" clearly describes the different strategies and their pros and cos.
NOTE: After the application of BPS10 (11.2.0.4.10) the default is now the Disk Failure Coverage rather than the Cell Failure Coverage.
그래서 디스크 용량 하나가 또 빠진다. 10.01 TB - 0.57TB => 9.4 TB
Step 4: Disk 그룹의 할당비율을 결정한다. 기본이 6;4 이므로 40% 가 recovery area를 위한 공간이 된다.
그래서 최종적으로 계산된 용량은 아래와 같다.
RECO Diskgroup => 3.76 TB
DATA Diskgroup => 5.64TB
출처 : http://pat98.tistory.com/793
Exadata Storage Space Calculation
How much usable storage a cutomer gets with every configurtion of the Exadata (quarter, Half or full Rack) is a little tricky for the customers guage.
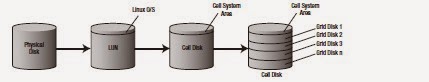
Now below diagram shows the Exadata disk architecture for every disk. The physical is virtualized as a cell disk and then a grid disk to be presented to the Disk groups. (i'll keep the disk architecture discussion for some later post)
now for all the cells the structure would be something like
Lets take the example and oracle Exadata quarter rack example ang calculate what exactly the customer gets in terms of storage space.
The Quarter Rack Consists of
- 2 DB nodes
- 3 Storage Cells
Now the 3 Storage cells ( with high performance disks) has the following configuration
Step 1: Calculate the RAW Storage
total Raw capacity => 12 disk on each cell * 600 GB each disk * 3 cells
=> 21600GB or 21.09TB
now 30 GB on the first two disks of every cell is reserved for Linux OS. So by default to a disk group is created with 30 GB of disk space from remaining 10 disks from every cell.
so we have a Disk Group name DBFS => 10 disks from each cell * 30 GB from each disk *3 cells
DBFS => 900 GB
so We are left with 570GB on each disk i-e a total of "20520 GB" or 20.03TB
Step 2: Now consider the mirroring requirement
After NORMAL Redundancy (i-e double mirroring) Avialable RAW CAPACITY 20.03/2 = 10.01TB.
Step 3: Reserve free space for fault tolerance.
with Disk failure coverage (DFC) one disk of 600GB is required to protect against the failure of one disks in a cell.
NOTE: that is a very important part. You need to plan for a Disk failure coverage or for complete cell node failure coverge. The ORACLE support document "Understanding ASM Capacity and Reservation of Free Space in Exadata (Doc ID 1551288.1)" clearly describes the different strategies and their pros and cos.
NOTE: After the application of BPS10 (11.2.0.4.10) the default is now the Disk Failure Coverage rather than the Cell Failure Coverage.
This means that available is 10.01 TB - 0.57TB (i-e 600GB) => 9.4 TB
Step 4: Decide the proportion of the Recovery Area. For example 60/40 (40% for recovery area)
So the Recovery area size (RECODG) would be => 3.76 TB
and the DATADG would be => 5.64TB
Half일 경우
Cell서버갯수(A) = 7
Disk 크기(B) : 600GB (high performance)
전체 용량(C) = B * 12EA * A = 50,400G
각셀에 필요한 용량(D) = OS영역 (30G * 2EA) + DBFS영역 (30G * 10EA) = 360G
ASM에 할당가능한 용량(E) = C - ( D * A ) = 47,880G
DATA그룹와 RECO그룹비율이 8:2일경우
DATA그룹 총 용량(F) = E * 0.8 = 38,304GB
RECO그룹 총 용량(G) = E * 0.2 = 9,576GB
Failure Group크기는
DATA그룹의 Failure Group(H) = F/A = 5,472G
RECO그룹의 Failure Group(I) = G/A = 1,368G
여기서 계산된 failure group크기는
ASM을 Mirror로 설정할시 요구되는 공간으로,
cell 서버 장애시 reblance되는 공간으로 사용됩니다.
Normal Redanduncy일경우
DATA그룹의 usable size: (F - H) / 2 = 16,416G
RECO그룹의 usable size: (G - I) / 2 = 4,104G
(1GB=1000000000 byte이므로 약 953M임)
실제 사용가능한 사이즈는
DATA그룹의 usable size: 16,416G * 0.953 = 15,644GB
RECO그룹의 usable size: 4,104G * 0.953 = 3,911GB
출처 : http://kosate.tistory.com/154
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- 금연
- DNA
- 유전자
- 흡연
- 부작용
- 100일
- 보건소
- 챔픽스 후기 금연
- oracle
- 상식
- 지진
- 뇌
- 냄새
- 과학
- 챔픽스
- 통신
- 금연일기
- 단백질
- 의료
- 금단증상
- 챔픽스 후기
- 설탕
- 믹스커피
- java
- 보건
- 생명과학
- 다이어트
- 윈도우10
- 오라클
- 인공지능
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |